Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer: Overview
In this topic, we will study the process of heat transfer from one system to another. It also explains the convection, conduction and radiation along with some thermal conductivities of some materials with the help of illustrations and graphs.
Important Questions on Heat Transfer
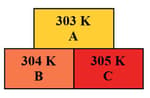
In the given diagram, the possible direction of heat energy transformation is
A deep pond of water has its top layer frozen during winter. The expected temperature of the water layer at the bottom of the pond is zero degree Celsius.
A deep pond of water has its top layer frozen during winter. The expected temperature of the water layer at the bottom of the pond is _____ degree Celsius.
Opening the door of a refrigerator makes the room to:
The rate of heat loss at $t=600$ sec after the heater is switched off (as in table- ) is
By varying the voltage applied to the kettle, you can change power consumption . Depending on the of kettle, water can be heated to different maximum temperatures. This dependence is shown in table.
| Table | ||||
| Power | ||||
| Temperature |
If the power consumption is
A steel drill making is used to drill a hole in a block of steel. The mass of steel block and the drill is each. The entire mechanical work is used up in producing heat such that the rate of rise of temperature of the system is . If is the couple required to drive the drill then, find its value in SI units.
A certain bullet of mass melts at and has specific heat as and a heat fusion of . The heat needed to melt the bullet if it was originally at , can be written as . Then the value of is.
Specific heat of a substance varies with absolute temperature as s where
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of substance from to can be written as . Find the value of , where and are integers.
A cube of iron (density , ) is heated to a high temperature and is placed on a large block of ice at . The cube melts the ice below it, displaces the water and sinks. In the final equilibrium position, its upper surface just goes inside the ice. If the initial temperature of block is then find the value of . .
The fastest mode of transfer of heat is
A sphere and a cube of same material and same volume are heated up to same temperature and allowed to cool in the same surroundings. The ratio of the amounts of radiations emitted in equal time intervals will be
A solid copper cube of edges is suspended in an evacuated enclosure. Its temperature is found to fall from to in . Another solid copper cube of edges , with similar surface nature, is suspended similarly. The time required for this cube to cool from to will be approximately
The rectangular surface of area of a black body at a temperature of emits energy at the rate of E per second. If the length and breadth of the surface are each reduced to half of the initial value and the temperature is raised to , the rate of emission of energy will become
Rate of heat loss of a body is 'K' time temperature difference between body and environment. Time taken by body in losing of the maximum heat it can lose is -
Assertion: A body at higher temperature always contains more heat.
Reason: Heat is energy that flow from a high temperature body to a low temperature body.
Assertion: Two bodies at different temperatures, if brought in thermal contact do not necessary settle to the mean temperature.
Reason: The two bodies may have different thermal capacities.
Two rigid identical spheres of same material, are in a closed chamber. The walls, floor and ceiling are thermally non-conducting. The thread with which sphere 2 is hanging is also non-conducting.
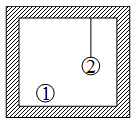
Assertion: Sphere will absorb more heat than sphere for the same temperature rise from to
Reason: Heat supplied to a system is used to raise the internal energy and do work against the external forces.